Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Lu via the
Lu via the  Yb(n,
Yb(n, )
) Yb
Yb
 Lu process
Lu processHashimoto, Kazuyuki; Matsuoka, Hiromitsu; Uchida, Shoji*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 255(3), p.575 - 579, 2003/03
Times Cited Count:42 Percentile:91.79(Chemistry, Analytical)The 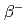 emitter
emitter  Lu is a promising therapeutic radioisotope for the treatment of cancer. It has a half-life of 6.73 days and maximum
Lu is a promising therapeutic radioisotope for the treatment of cancer. It has a half-life of 6.73 days and maximum 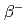 energy of 498 keV, resulting in a short range of radiation in tissue. The decay is accompanied by the emission of low energy
energy of 498 keV, resulting in a short range of radiation in tissue. The decay is accompanied by the emission of low energy  -radiation with
-radiation with 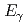 = 208 keV (11.0%) and 113 keV (6.4%) suitable for simultaneous imaging. Lutetium-177 can be usually produced at nuclear reactors with high yield and high specific radioactivity by the
= 208 keV (11.0%) and 113 keV (6.4%) suitable for simultaneous imaging. Lutetium-177 can be usually produced at nuclear reactors with high yield and high specific radioactivity by the  Lu(n,
Lu(n, )
) Lu reaction. However, radioisotopes with higher specific radioactivity are required in the field of radioimmunotherapy using labeled monoclonal antibodies. Thus, an alternative production route, namely the
Lu reaction. However, radioisotopes with higher specific radioactivity are required in the field of radioimmunotherapy using labeled monoclonal antibodies. Thus, an alternative production route, namely the  Yb(n,
Yb(n, )
) Yb
Yb 
 Lu process was studied to produce no-carrier-added (nca)
Lu process was studied to produce no-carrier-added (nca)  Lu in this work. The radiochemical separation of the nca
Lu in this work. The radiochemical separation of the nca  Lu from the macroscopic ytterbium target was investigated by means of reversed-phase ion-pair HPLC. The nca
Lu from the macroscopic ytterbium target was investigated by means of reversed-phase ion-pair HPLC. The nca  Lu was obtained in radiochemical pure form with a separation yield of 80%.
Lu was obtained in radiochemical pure form with a separation yield of 80%.
 Mo/
Mo/ Tc separation-concentration apparatus based on solvent extraction and column chromatography
Tc separation-concentration apparatus based on solvent extraction and column chromatographyTsuchiya, Kunihiko; Suzuki, Yoshitaka; Nishikata, Kaori; Shibata, Akira; Nakamura, Natsuki; Tanase, Masakazu*; Shiina, Takayuki*; Ota, Akio*; Kawabata, Masako*; Takeuchi, Nobuhiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Mo/
Mo/ Tc
TcHu, X.; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Wang, X.*; Wang, H.*; Fujita, Yoshitaka; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
no journal, ,
Technetium-99m ( Tc) stands as the most widely employed radionuclide for nuclear medicine diagnostic imaging procedures.
Tc) stands as the most widely employed radionuclide for nuclear medicine diagnostic imaging procedures.  Tc originates from the radioactive decay of molybdenum-99 (
Tc originates from the radioactive decay of molybdenum-99 ( Mo). In present study, four inorganic ion exchangers were synthesized by combining SnCl
Mo). In present study, four inorganic ion exchangers were synthesized by combining SnCl with SbCl
with SbCl , WO
, WO Cl
Cl , WO
, WO , and TiCl
, and TiCl in a one-to-one for application to the separation of
in a one-to-one for application to the separation of  Tc and
Tc and  Mo by column chromatography approach. We conducted comparing and evaluating their respective Kd (distribution coefficient) values. We utilized these synthesized inorganic ion exchangers for adsorption in a solution with a prepared concentration of 4 ppm of Mo/Re, where Re acted as a surrogate element to simulate Tc. Various pH environments ranging from 2 to 12 were prepared. Subsequently, we conducted adsorption experiments using batch testing and determined the Kd values. The results revealed that all four ion exchangers exhibit commendable selectivity and relatively high Kd values, with SnCl
Mo by column chromatography approach. We conducted comparing and evaluating their respective Kd (distribution coefficient) values. We utilized these synthesized inorganic ion exchangers for adsorption in a solution with a prepared concentration of 4 ppm of Mo/Re, where Re acted as a surrogate element to simulate Tc. Various pH environments ranging from 2 to 12 were prepared. Subsequently, we conducted adsorption experiments using batch testing and determined the Kd values. The results revealed that all four ion exchangers exhibit commendable selectivity and relatively high Kd values, with SnCl -TiCl
-TiCl demonstrating the highest Kd.
demonstrating the highest Kd.